Hardware TDR Ethernet cable diagnostics
Starting with KeeneticOS version 3.7, the TDR hardware diagnostics of Ethernet cables is available. The function works on the built-in 8-port RTL8370 series. It supports diagnostics on the LAN ports and does not work on the WAN (blue) port. Yet if you configure a LAN port as a WAN port, then the diagnostic on that port is still supported.
In Keenetic KN-1811 model, hardware TDR diagnostics works on the high-speed 2.5 Gbit/s network port only.
TDR (Time Domain Reflectometer) — a tool for detecting faults in cable lines using the locator (reflectometry) method. The TDR test helps identify the nature of the problem and the approximate distance to a twisted-pair Ethernet cable.
In the router's web interface, go to the Diagnostics menu, select a port on the Cable Diagnostics tab, and click the Test button. The Pulse Reflectometry Diagnostic Test (TDR) results on the selected interface will be displayed below.
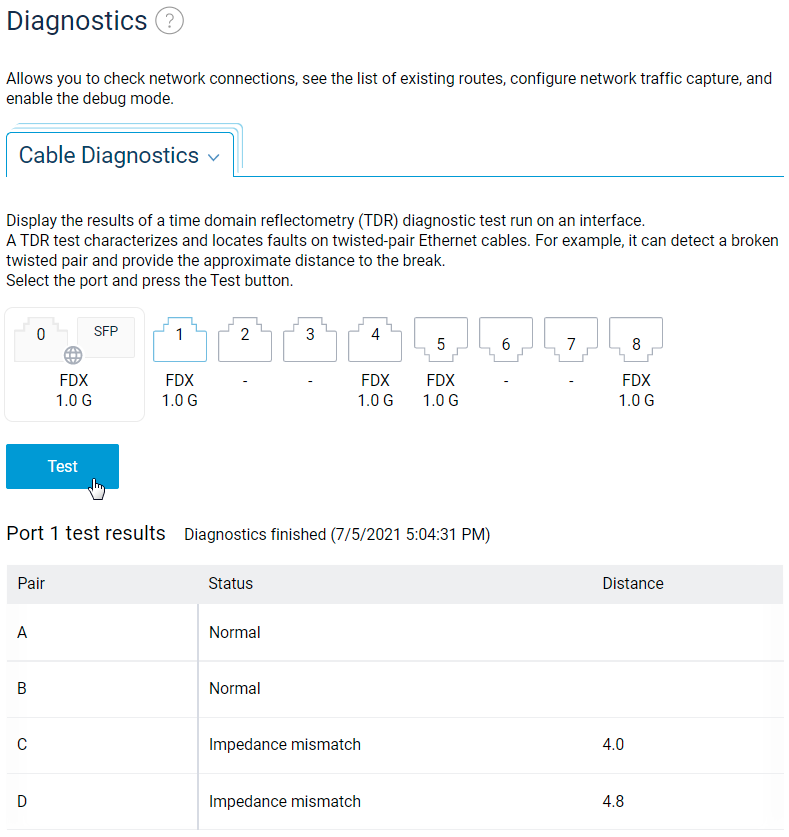
Test statuses:
Normal — The pair is connected, and no problems are detected;
Not Connected — No contact with the terminal device. This may indicate an unconnected cable; a faulty or low speed port on the terminal device; or a break in the pair's conductors;
Shorted — The twisted-pair wires are short-circuited;
Impedance mismatch — Possible causes of impedance mismatch are: twisted pair not properly crimped (reversed conductors); damaged pair conductors; defective connector at end of cable;
No signal — The other end of the pair is connected to the port with the power off. This usually means that there is no problem with the pair itself;
Distance — The distance to the fault in metres. If no problems are found in the pair, this value is
0.
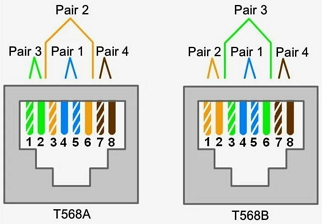
The twisted pairs A, B, C, D is equivalent to 1, 2, 3, 4:
Important
Please note the following points:
— When the terminal device connected to the router is in active state (port powered and working) and the test status is displayed as Normal, then no cable distance will be determined. To determine the distance (cable length), you must e.g. pull the cable out of the terminal device port, simulating a cable break and run the test again.
— Cable diagnostics is also supported on aggregated ports.
— When diagnosing one port, communication with the terminal devices is not interrupted on the other ports.