Internal service traffic
Keenetic routers generate service traffic during their work. The network traffic occurs periodically or constantly in the background, initiated by the router itself. This is traffic from internal system processes, services, and applications that are automatically enabled on the router, not initiated by the user.
With the default settings, the sources of service traffic from the router can be:
Authentication and licensing service;
Diagnostic module;
Automatic update function;
Cloud services agent RMM and KeenDNS;
Service for mobile application;
The mechanism for Internet connection status monitoring (Internet Checker);
The adjustable mechanism for network connection status checking 'Ping Check' (it turns on automatically only when a USB modem is connected);
Time synchronization protocol.
All service traffic, except for the Service for mobile application module traffic, is directed to the servers allocated in the *.keenetic.ru domain. However, the destination IP addresses of the service traffic might resolve to domain names in the *.omni.ru domain. The Service for mobile application module contacts the servers in the *.keenetic.cloud domain.
Below is a table showing the service traffic used by different Keenetic router services. The figures are for the 24/7 operation of the router on default settings. Below the table, you will find a brief description of the services, from which you may learn what they are used for, how they work, and how to turn some of them off to reduce the amount of service traffic.
Traffic source | Is it enabled by default? | Can it be turned onand off? | Traffic volume per day/month |
|---|---|---|---|
Authentication and Licensing Service | Yes | No | Up to 10 KB / up to 300 KB |
Diagnostic module | Yes | Yes | Up to 3 KB / up to 100 KB |
Automatic update function | Yes | Yes | Firmware size depends on the model and component set (8 to 20 MB on average) |
Cloud services agent RMM and KeenDNS | Yes | Yes | 794 KB / 24 MB |
Service for mobile application | Yes | Yes | about 40 MB (if the mobile device is added to the cloud) |
The mechanism for Internet connection status monitoring (Internet Checker) | Yes | Yes | 3.3 MB / 100 MB |
The adjustable mechanism for network connection status checking (Ping Check) | No; automatically activated only when a USB modem is connected to the router | Yes | 5.5 MB / 170 MB (in 'Automatic' mode with TCP verification); 1.62 MB / 50.22 MB (with ICMP verification) |
Time synchronization protocol | Yes | Yes | 400 bytes / 1.6 KB |
Authentication and licensing service (always on, cannot be turned off).
When Keenetic connects to the Internet, the unique service code of the device, KeeneticOS version, selected update channel and the IP address are transmitted. The information is sent to the server via the secure
HTTPSprotocol within a minute after turning on the router, when the WAN IP address is changed, and once per day when there is no IP address change. One request is up to10 KB.This information is used to:
authenticate your device to receive updates and access Keenetic services;
determine the warranty period by the date of the first connection to the Internet;
automatically obtain an SSL certificate, validated by Certificate Authority, from the keenetic.io domain for secure access to the web interface of your device. The amount of traffic when receiving a certificate is approximately
180 KB. The certificate automatically renews every three months;regularly transmit the device IP address for KeenDNS service operation;
regularly transmit the KeeneticOS version and update channel for automatic update service operation and user notification in the device web interface.
Diagnostic module (enabled by default, can be disabled).
The diagnostics module generates reports on errors and critical system failures and sends them to the server via
HTTPSsecure protocol as they accumulate. Each report is no larger than10 KB. The report can include information about system resource usage, protocols and Internet connection types, and USB device identifiers.These reports allow our technical support team to diagnose problems more accurately when users contact our technical support and allow developers to continuously analyze and improve the stability of Keenetic devices and services.
If you want to share this info, you can enable the report sending function in the web interface, on the General System Settings page, under Product Improvement Programme.

Automatic update function (enabled by default, can be disabled).
The function sends a request to the server via a secure HTTPS protocol to build the operating system in the required configuration for the device, then receives the resulting file and updates it in the device memory with the subsequent reboot. The frequency of official releases is about
6-10times a year. The amount of traffic depends on the number of operating system components. On average, when using the recommended set, the download size ranges from8 MB(for entry-level models) to20 MB(for advanced models).You can disable the automatic update function in the web interface, on the General System Settings page, under KeeneticOS Update and Component Options. In this case, the device will not perform the update without your participation.
Cloud services agent (enabled by default, can be disabled).
The agent is needed to remotely access the Keenetic router via the KeenDNS domain name service and when using the Netcraze RMM cloud service.
The agent uses the UDP keep-alive mechanism to check and maintain a constant connection between the router and the server. The polling occurs every
17seconds.UDP/9requests of160 byteseach are used — that's794 KBper day or24 MBper month. Once the router is turned on, a request to check servers on portUDP/4044is used.If you are not using the KeenDNS domain name on your router, disable the service to reduce service traffic. Remove the agent component from the device's operating system. You can do this on the General System Settings page, under KeeneticOS Update and Component Options by clicking Component options.
Please note that the SSTP VPN Server and WebDAV Server components depend on Cloud services agent. To uninstall the agent, you will also have to uninstall these dependent components too.
Service for mobile application (enabled by default, can be disabled).
The module provides remote access to the device from the Keenetic mobile application. Every
30 seconds, it reports to the cloud controller on the Keenetic Cloud servers. The module only starts sending data when there's a device added to your account. Data sent consists of system events (Internet connection change, router restart, etc.) and telemetry on traffic, CPU and memory load. The data is transmitted in encrypted form using theAESandCurve25519technologies and is stored in compliance with the legislation on protecting personal data. Daily traffic is about40 MBwhen added to the cloud service.If you are not using remote access to the router via the mobile app, disable the Keenetic Cloud service to reduce service traffic. You can do this in the web interface, on the General System Settings page, under Cloud Service for Mobile Applications.
To completely disable the Keenetic Cloud service, remove the Service for mobile application component from your device's operating system. You can do this on the General System Settings page, under KeeneticOS Update and Component Options, by clicking Component options.
Internet connection status monitoring (Internet Checker) (enabled by default, can be disabled).
The Internet Checker module provides the system mechanism for checking the availability of the Internet. Its uses include the control of the
 LED indication on the device body (lit — Internet connection established, off — no connection to the Internet).
LED indication on the device body (lit — Internet connection established, off — no connection to the Internet).No data is transferred, with requests made every
15 secondsvia theDNS/53+TCP/80connection. One request is580 bytes, about3.3 MBper day or100 MBmonthly.The module also requests the server every
40 secondsusingTCP/80and once every10 minutesusingDNS/53, with no data transfer. One request is500 bytes, which is approximately735 Kbytesper day or22 Mbytesper month.You can disable Internet Checker via the command-line interface (CLI) of your Keenetic.
To disable it, run the following commands:
no service internet-checkersystem configuration saveAfter disconnecting, the Internet connection will be checked by ARP polling the default gateway (local traffic will be used).
Network connection status checking (Ping Check) (disabled by default, turns on automatically only when a USB modem is connected; otherwise, it is turned on by the user).
Ping Check can be used to help ensure connection redundancy and features automatic power control of USB modems. Module operation is entirely configurable via its parameters: the checking type (ICMP requests or TCP port check), the interval between checks, and the number of failed checks.
When using the default Automatic check mode, the module polls the server with the Check interval (time in seconds between checks) of
10 seconds. The default value of the Trigger threshold (number of unsuccessful checks) is5. The module establishesDNS/53+TCP/443connection without transferring data. One request is650 bytes, which is5.5 MBper day or170 MBmonthly.You can disable Ping Check via the web interface on the connection type page (Mobile, Ethernet, Wireless ISP, DSL connection) on which it is enabled. Under Check the Availability of the Internet (Ping Check), set the Mode field to Disabled.
If you want to leave Ping Check enabled, you can use ICMP protocol to reduce service traffic. ICMP requests will be less in traffic volume: one request will be
200 bytes, which is1.62 MBper day or50.22 MBper month.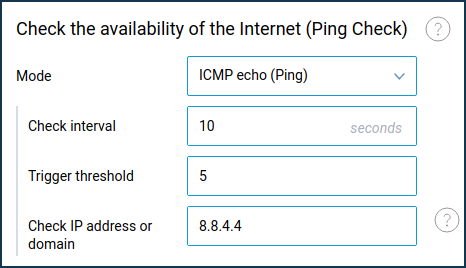
For more information, see the Ping Check fine-tuning manual.
NTP time synchronization (enabled by default, you can disable or change the preset interval).
The service automatically sets the time in the router. The Set time automatically option is enabled by default. By default, the device attempts to synchronize with the Keenetic server immediately after powering on and sends a request every
10 secondsuntil it successfully synchronizes. The request takes place over the NTP protocol.DNS/53+NTP (UDP/123)are used. The amount of traffic used for time synchronization is400 bytes.After the clock is synchronized, the time is counted by the internal counter, and the next synchronization will be done in
7 days. The time synchronization service uses only1.56 KBper month.We do not recommend that you disable this service. If necessary, you can increase the synchronization interval to
28 days. To do this, in the Keenetic command-line interface (CLI), run the following commands:ntp sync-period 40320 system configuration saveSummary
The Keenetic router uses service traffic for its internal system services. It automatically transmits information about your device over the Internet only for technical support and warranty service and accesses the servers of our online services. We do not collect information about websites you visit, search engine queries or any other personal information in full compliance with the Personal Information Protection Act.
The router itself cannot block access to Keenetic Cloud servers and core system services unless you disable them as described above. These connections are necessary for stable, secure operation of the router and reliable assessment of its performance by the cloud services. The operation of these services does not architecturally imply any permanently open ports and backdoors that intruders can use. Connections are established in short secure sessions, and no outside scanners will see open ports or vulnerabilities.
The bulk of service traffic is used by Internet availability and network connectivity checking mechanisms (Internet Checker and Ping Check) and cloud service agents. We remind you that Ping Check is automatically activated only when a USB modem is connected. Keep it in mind if you use the Internet tariff with a small amount of provided traffic, which has to be saved.
If you notice excessive Internet traffic consumption, the first thing to look at is user traffic. Today's operating systems and applications actively use various online services and can generate a significant amount of traffic from devices connected to your Keenetic router in the background. You can get detailed information about the traffic consumption of your connected devices over the past
24 hoursfrom the device's traffic monitor.