Connecting to an L2TP/IPSec VPN server from Android
Important
If you want to configure a Keenetic router as a VPN server, make sure that it has a public IP address, and when using the KeenDNS service, that it works in the 'Direct access' mode. If any of these conditions are not met, connecting to such a server from the Internet will be impossible. The exception to this rule is described in the Note section below.
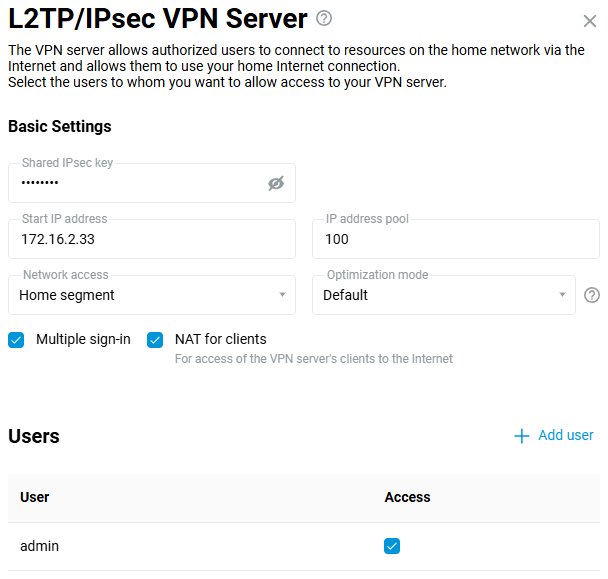
Configure the VPN server according to the instructions L2TP/IPSec VPN server. For example:
Then set up an L2TP/IPSec connection on your Android mobile device.
Important
The support for the IPSec Xauth PSK client was present in Android until version 11. Since version 12, only IKEv2 and IPSec tunnel support remains (some vendors and phone manufacturers have a different list of supported tunnels).
On the 'VPN' screen, add a new entry.
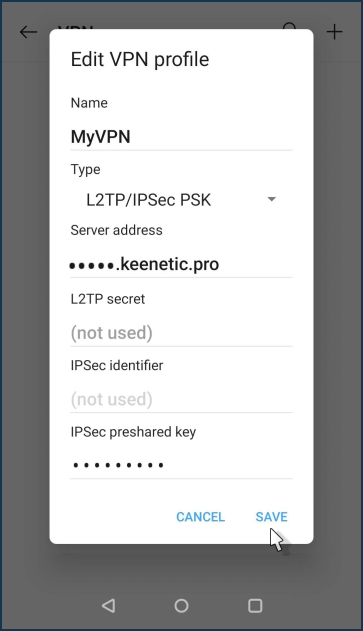
Specify the name and connection type 'L2TP/IPSec PSK'. The server address is the public IP address of the router or its KeenDNS domain name, and enter the preshared IPSec key previously installed on the VPN server. Save the connection settings.
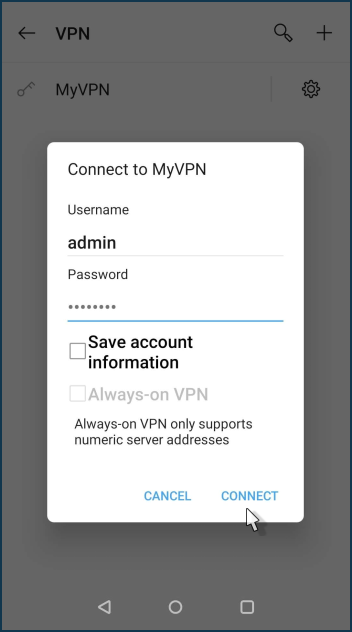
Click on the created connection.

Enter the username and password of the router user account with permission for the VPN connection. Click the 'Connect' button.
After that, the VPN connection to the L2TP/IPSec server on the Keenetic router will be attempted.
To view the connection state, click on the VPN connection entry.

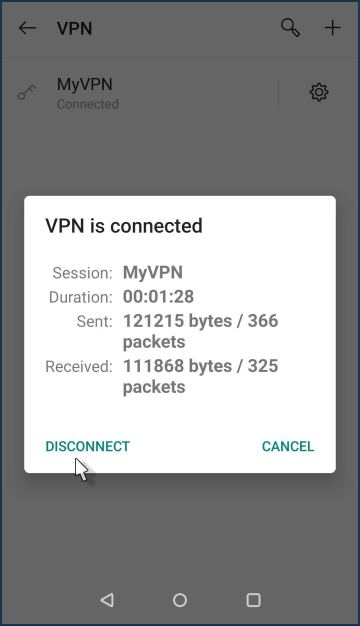
You can disable the VPN connection on the same screen by clicking the 'Disconnect' button.
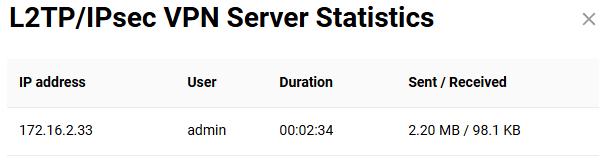
When a VPN connection is running, you can see statistics of current connections on the Keenetic router.
Note
If your Keenetic router is located behind another router, you may need to do some extra steps to access the VPN server.
It is only possible to connect from the Internet to a VPN server with a private IP address if you have configured port forwarding on the upstream router with a public IP to the private IP address of Keenetic. L2TP/IPSec requires UDP 500 and UDP 4500 forwarding. Another option is to forward all ports and protocols, which is called DMZ on some routers.
A typical example of such a router is a CDC Ethernet 3G/4G USB modem. It can get a public address from the ISP and give a private address to the Keenetic router. Port forwarding setup depends on the USB modem. There are the ones that forward all ports without any adjustments, and some of them have this option in their own web interface. And there are the ones where it is not allowed at all.
Another example of such a router is an optical GPON ONT. In such devices, the forwarding is configured in their web interface.
If port forwarding is set up correctly, you can establish a VPN connection with the external public IP address of such a router. It will forward the connection to your Keenetic router's private address.