DLNA over VPN
Keenetic routers allow you to configure access to their DLNA media library via PPTP, L2TP/IPSec, and SSTP VPN tunnels.
Important
This method is only implemented for access to a DLNA server running on a Keenetic router. A VPN server must also be running on the same router.
Connection to the DLNA media library will only work from a device running a VPN client (the VPN connection must be established from that device). This device can be a mobile phone or a computer running iOS, Android, Windows, or macOS operating systems. If you use a Keenetic router as a VPN client, multicast transmission via VPN will not work.
At the end of the article, in the Note section, you will find additional information about implementing DLNA over VPN.
Configuration
On the Keenetic router, first configure the DLNA media library and a VPN server. If you have a public IP address on the router's external interface, use the PPTP or L2TP/IPsec VPN server. If you have a private IP address, enable the SSTP VPN server.
When configuring the VPN server, add a user or specify an existing one who will be allowed to access the local network through this VPN connection (in our example, we use L2TP/IPsec).

Then, go to the Users and Access page and, in the User Accounts section, click on the user you want to allow to use DLNA over VPN. In our example, permission is set for the user vpnuser01.

In the user settings window that appears, enable the DLNA over VPN option and save the settings. This setting allows for multicast to work through a VPN tunnel. No additional port forwarding is required.

Now, from the VPN client side, establish a connection to the VPN server on the router.
Important
The SSDP protocol announcement to the multicast address 239.255.255.250 is not performed immediately after establishing a VPN connection. It may take several minutes from when the VPN tunnel starts working. Launch a DLNA-compatible media player and check that it is working correctly.
As examples, we recommend using the following DLNA-compatible media players: VLC media player, MediaMonkey, or Emby.
Examples
Establish a VPN connection from your computer. Launch the VLC media player. Go to the View > Playlist menu and click Universal Plug'n' Play, in the Local Network section, to access shared media files. The DLNA server on the Keenetic router (in our example, it is Hopper SE) will appear in the player. Click on Browse Folders.
Select the content you want to play and start it.

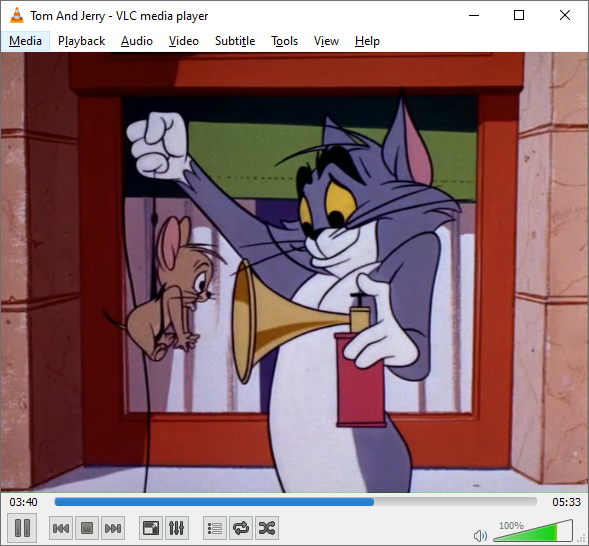
Another example from the MediaMonkey media player. Launch the application and navigate to the Devices & Services section. You will see the DLNA server on Keenetic. Open the Browse Folders folder, select the content you want to play, and then start it.

You can also access the DLNA media library from a mobile device.
This is an example of connecting from an Android smartphone. Establish a VPN connection to the router. A few minutes after setting up the VPN, launch the VLC app. In the Local Network section, you will see the DLNA server on your Keenetic router. Open the Browse Folders folder, select the content you want to play, and then start it.
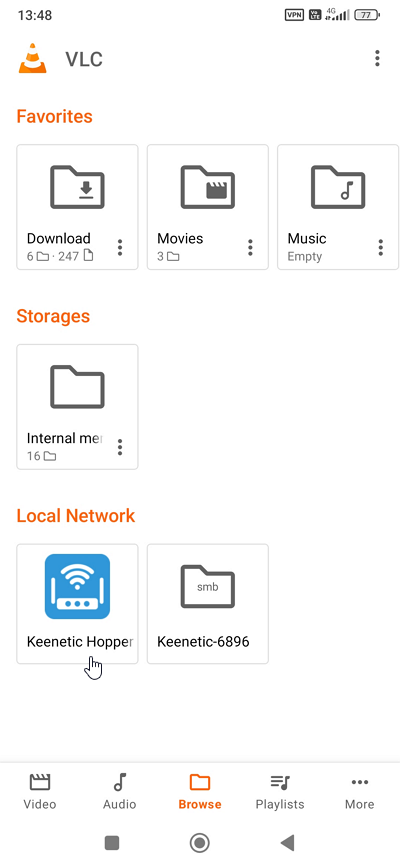
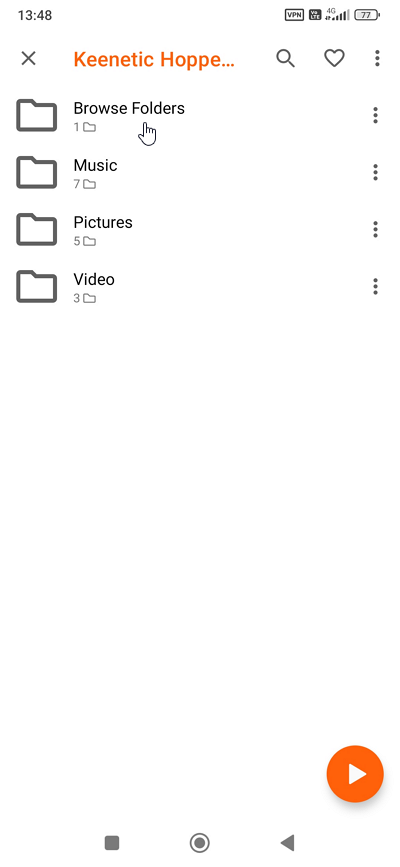


You can also use other mobile applications that support DLNA servers.
Note
DLNA is a set of standards that allows compatible devices to transmit and receive various media content (images, music, video) over a home network and display it in real time. In other words, it is a technology for connecting home computers, mobile phones, laptops, and consumer electronics into a single digital network. The medium for transferring media content is usually a home peer-to-peer local area network. The DLNA client and server must have IP addresses from the same subnet. When the DLNA client and server are on different subnets, content cannot be broadcast, but by tunnelling network traffic at the L3 level of the OSI network model and combining them into a single subnet, it has become possible to access the DLNA server via the Internet within a VPN connection.
Please note that DLNA was originally designed to be used within a single local network; therefore, DLNA operation over Internet channels via VPN is not a standard use case. In this scenario, we cannot guarantee the reliable operation of this feature, as several factors may impact its performance.
For DLNA to function, the client and server must be on the same subnet. DLNA does not allow NAT between devices. Since in our case the client and server are not on the same local network but in different locations, we use a VPN tunnel to combine them into a single subnet. Now DLNA will operate within the VPN connection. Interaction between the DLNA server and client occurs via the HTTP protocol. The DLNA client sends SEARCH broadcast requests within its network segment. Specifically, the client sends SSDP packets over the network to search for a DLNA server. When the DLNA server detects messages from the client, it interacts with the client directly. After selecting and launching a media file, data exchange via the TCP protocol begins. The client starts caching the media file and playing it in the media player.
The correct playback of content depends on the performance of the Internet channel on both the client and DLNA server sides, the reliability and stability of the Internet and VPN connections, network parameters (e.g., MTU size and network packet fragmentation), client performance, and other factors. When working through a mobile operator's network, it is challenging to ensure stable DLNA operation and high-quality playback of media content over the Internet.