Configuring firewall rules that use IP address ranges
Let's look at specific examples of how to configure firewall rules on a Keenetic router when you need to use an IP address range.
For theoretical information describing how a firewall works and examples, see the articles How does a firewall work? and Firewall rule examples.
When creating firewall rules via the web interface, you can choose a Subnet based on a subnet mask in the Source IP/Destination IP field.
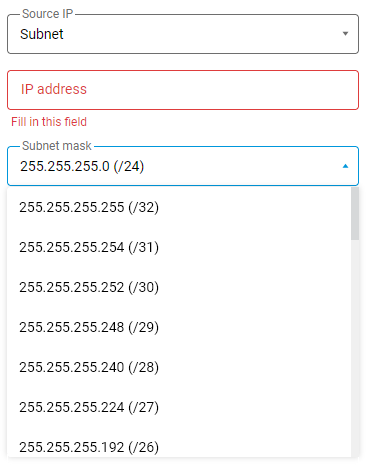
A subnet mask enables you to divide a network into multiple smaller networks (subnets), each with a specific number of addresses for hosts. A subnet is a logical division of an IP network. All hosts on the same network or subnet have the same subnet mask.
Here is a table showing the number of subnets and hosts for a 24-bit mask (255.255.255.0) for a class C network:
Subnet mask | Prefix | Number of subnets | Number of addresses for subnet hosts |
|---|---|---|---|
255.255.255.128 | /25 | 2 | 126 |
255.255.255.192 | /26 | 4 | 62 |
255.255.255.224 | /27 | 8 | 30 |
255.255.255.240 | /28 | 16 | 14 |
255.255.255.248 | /29 | 32 | 6 |
255.255.255.252 | /30 | 64 | 2 |
The mask 255.255.255.0 (/24) defines the entire Class C subnet, i.e. 254 addresses, while 255.255.255.255 (/32) allows you to specify a single network node.
There are many online IP calculators available on the Internet (e.g., https://ipnet.tools/ip-calculator) that allow you to calculate IP addresses and subnet masks quickly.
Let's look at some examples.
1.1. Suppose you need to deny TCP access to hosts on the local network with IP addresses in the range 192.168.100.33 – 192.168.100.46 (14 hosts).
The firewall rule for our example will look like this (the rule is applied to the Home interface):

The subnet 192.168.100.32 with a mask of 255.255.255.240 (/28) allows you to allocate a logical subnet with 14 working addresses (the IP address of the first host is 192.168.100.33, the IP address of the last host is 192.168.100.46).
1.2. Suppose that you want to use the IP address range 192.168.1.65 — 192.168.1.126 (62 hosts) in the rules. In this case, you should use the network mask 255.255.255.192 (/26). In the firewall rule, you need to specify the address 192.168.1.64 and the mask 255.255.255.192.
1.3. Suppose that the rules require the use of the IP address range 192.168.1.201 — 192.168.1.206 (6 hosts). In this case, you should use the network mask 255.255.255.248 (/29). In the firewall rule, specify the address 192.168.1.200 and the mask 255.255.255.248.
Tip
If you need to use a wider range of IP addresses that cannot be allocated with a single mask (for example, 192.168.1.33 — 192.168.1.70), you can use several firewall rules: 1st rule for the IP address 192.168.100.32 and the mask 255.255.255.224, and the second rule for the IP address 192.168.100.64 with the mask 255.255.255.248.
Important
If you use both allow and deny rules in your firewall rule set, the allow rules must be placed above the deny rules. First, create allow rules for specific addresses or subnets, and then create deny rules.